AIOps in the Cato SASE Platform: Using Predictive AI Networking to Shift from Reactive to Proactive IT
It was a quiet Monday morning until John, head of IT, opened his laptop and saw 424 new support tickets. Users across the office were reporting issues like “apps won’t load” and “internet not working.” After hours of investigation that stretched into the next day, the team traced the problem to a branch router overwhelmed by malformed DNS queries from a misbehaving IoT device. The router’s CPU was maxed out, delaying DNS resolution and disrupting connectivity for everyone. Just as they resolved that, 45 more tickets came in from the sales team. Their computers were freezing due to a beta app installed after a CRM recommendation, which caused memory leaks and high CPU usage across devices, requiring even more time to fully diagnose.
These imaginary but realistic examples show how everyday actions, even without malicious intent, can cause major disruption. With AIOps, bandwidth spikes could have triggered early alerts, and CPU issues might have been quickly linked to the faulty app or device. Instead of reacting under pressure, the IT team could have prevented the impact altogether. That’s the power of AIOps and predictive AI networking: it transforms chaos into insight and enables control before problems escalate.
What is AIOps?
AIOps, or Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations, uses machine learning, automation, and data analysis to help IT teams monitor and manage modern infrastructure more effectively. By analyzing complex system signals in real time, AIOps can detect patterns, predict issues like CPU overloads, bandwidth congestion, application performance degradation, and takes action before users are affected. Beyond early detection, AIOps also helps assess the scope and potential impact of problems. It can trace issues back to their root causes, identify which systems or critical applications are affected, and forecast how the situation may evolve. This shift allows IT teams to move from reactive troubleshooting to proactive problem prevention, and data-driven problem prevention. Various industry studies and expert analyses suggest that the most effective AIOps solutions can detect and resolve operational issues before they are formally identified by IT teams.
Why IT Ops Needs AIOps: Key Challenges It Solves
- Manages Complexity: Unifies cloud, legacy, and hybrid environments.
- Reduces Noise: Filters alerts and highlights what matters.
- Automates Routine Tasks: Replaces slow, error-prone manual work.
- Prevents Issues: Detects CPU spikes, app slowdowns, and bandwidth overloads early.
- Speeds Up Resolution: Combines fast anomaly detection with trend-based prediction and root cause analysis to reduce MTTR and address issues before they fully develop.
- Ensures Compliance: Supports NIS2, DORA, ISO 22301, and ITIL 4 while also identifying trends, such as the increasing use of unsanctioned apps, that could lead to compliance violations over time.
- Protects SLAs: Forecasts risk and helps teams act before thresholds are breached.
AIOps Research: Detection and Predictive AI Networking in the Cato SASE Platform
Predictive Insights Powered by Unified Visibility in Cato’s Architecture
Our AIOps research was deeply rooted in a key architectural advantage: full visibility. Through our Cato SPACE (Single Pass Cloud Engine) architecture, we maintain a unified context across all devices and network flows within the Cato SASE Platform. This cohesive view allows us to continuously monitor CPU usage, memory load, bandwidth consumption, application-level behavior, and more at scale.
This rich dataset powers our ongoing work in anomaly detection and predictive analytics. By identifying unusual trends in resource usage, such as sudden or sustained increases in CPU or bandwidth, we can forecast potential issues before they become real disruptions. Our models focus not just on raw values, but on how future usage may exceed critical thresholds, enabling early intervention.
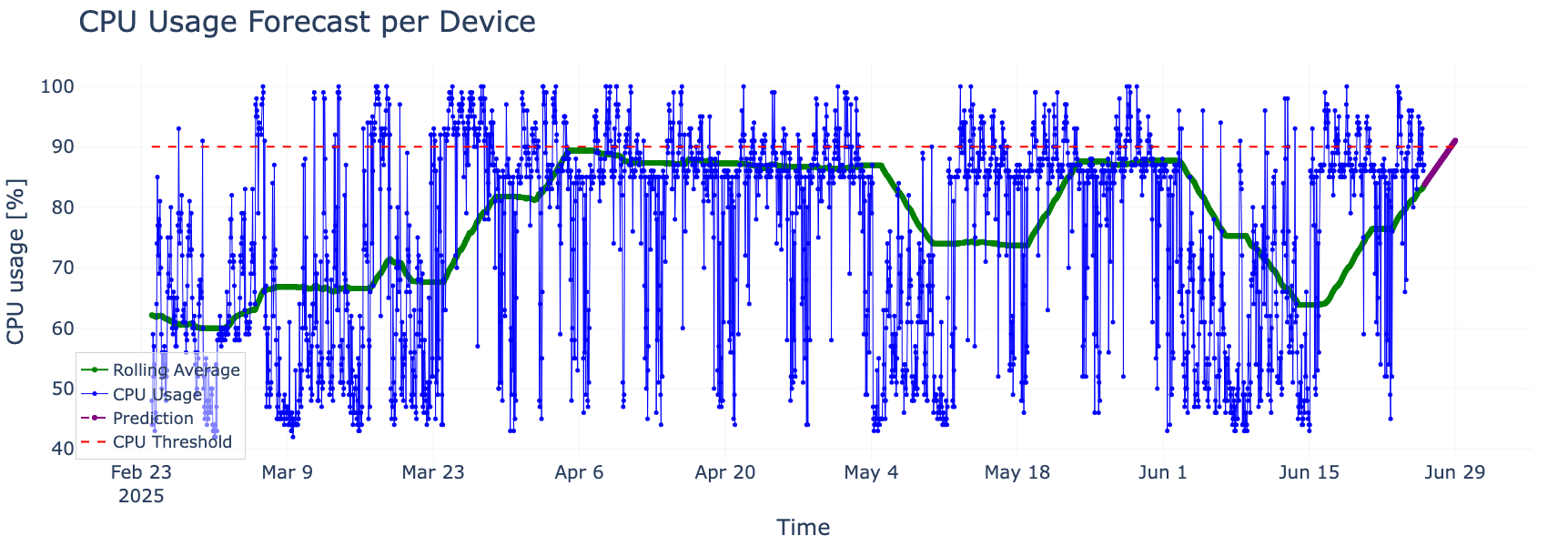
For example, in the graph below (Figure 1), we illustrate how predictive AI networking detects that projected CPU usage on a monitored system is expected to exceed a predefined 90% threshold within two days. This prediction is not just based on observed data, but also contextualized against limits that matter operationally. This ensures the alert is meaningful and actionable.
A forecasted spike in CPU utilization shows projected values crossing a predefined threshold (red dashed line). The blue line represents raw hourly CPU usage, while the green line smooths this data to highlight underlying trends. Combined with predictive modeling (purple line), this approach enables early, context-aware alerts that help prevent performance degradation.
Figure 1. CPU Usage Forecast Per Device
Correlating Application Traffic with Device-Level CPU Load
In root cause analysis, when diving into a specific device, we explore the relationship between application traffic and system performance. By analyzing correlations between upstream and downstream throughput and CPU usage, we uncover valuable insights into which applications may be contributing most to resource load. Several operational factors can influence this relationship.
On the downstream side, certain traffic types can drive high CPU usage on the device. Examples include high-resolution video streaming, real-time dashboards, and encrypted cloud traffic that requires local inspection. Large file downloads, software updates, and asset streaming also trigger intensive post-download processing like decryption, scanning, or rendering. These activities turn passive data consumption into a significant device-level workload.
On the upstream side, sustained outbound traffic such as log uploads to monitoring systems, video conferencing streams, file synchronization with cloud storage, or IoT sensor data transmissions can place a significant load on the CPU. These flows often involve encryption, policy enforcement, session management, and deep inspection, all of which consume processing resources.
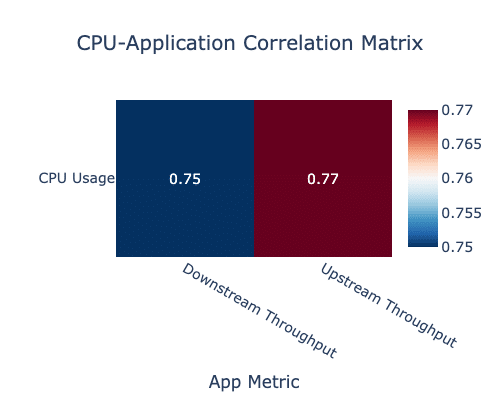
As shown in Figure 2, this type of correlation analysis helps guide root cause investigation and capacity planning without requiring manual guesswork. A correlation matrix reveals a strong statistical relationship (greater than 0.7 on a scale from -1 (perfect negative linear correlation) to 1 (perfect positive linear correlation) between an application’s data throughput and the system’s CPU load, suggesting the app may be driving increased resource usage.
Figure 2. Network and CPU Correlation
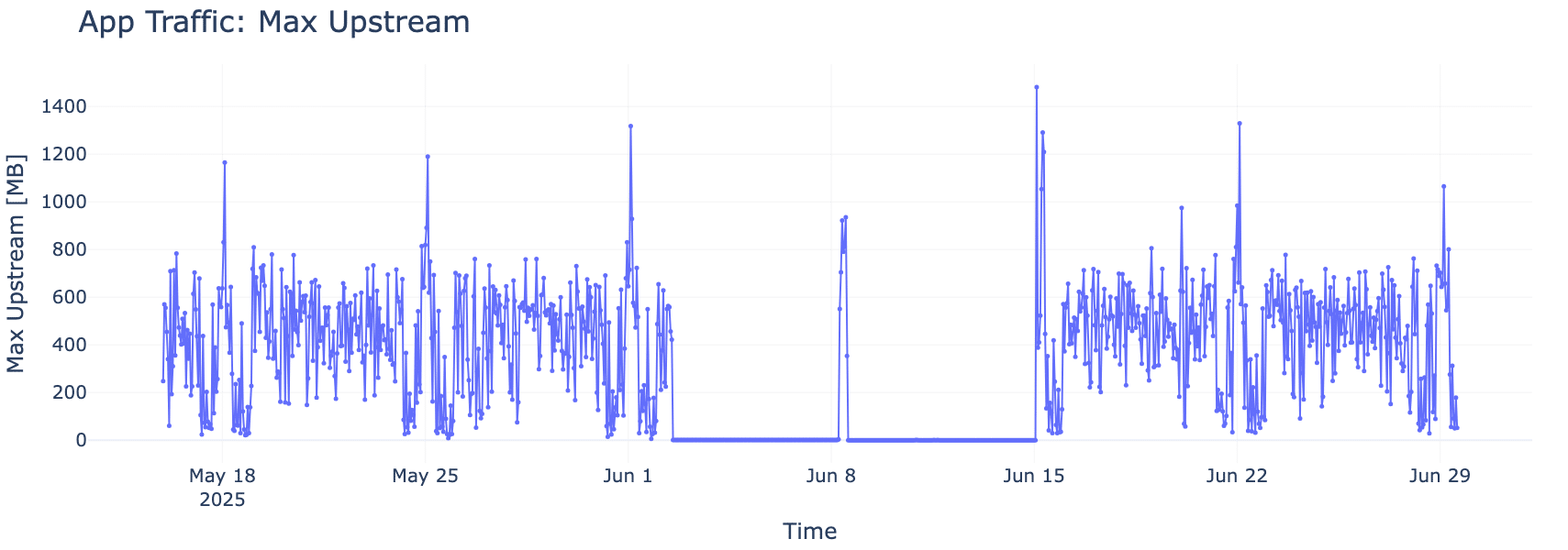
Sometimes, timing tells the story. In Figure 3, we observe that when a customer application’s upload activity drops, a corresponding decrease in CPU usage follows. Even though CPU data can be noisy due to many processes running simultaneously, clear trends emerge. These kinds of observations help us pinpoint which apps are impacting performance most.
A visible drop in both upstream traffic and CPU usage over the same timeframe highlights the application’s influence on system load, offering critical clues for optimization.
Figure 3. Application Activity vs. CPU Load (Megabytes)
Beyond Traffic: Identifying Other Drivers of CPU Load
Beyond traffic direction, there are additional contributors to CPU load. Spikes in the number of connected hosts or concurrent flows, such as during login storms or mass software updates, can overwhelm session tracking and enforcement engines. High-volume or compute-heavy applications, including malware scanning or large file transfers, also consume significant processing power. In some cases, newly deployed software versions may introduce performance regressions or excessive logging. Additionally, configuration changes like enabling deep packet inspection, zero trust policies, or intrusion prevention features increase per-packet processing demands.
Predictive Bandwidth Modeling for Proactive Resource Management
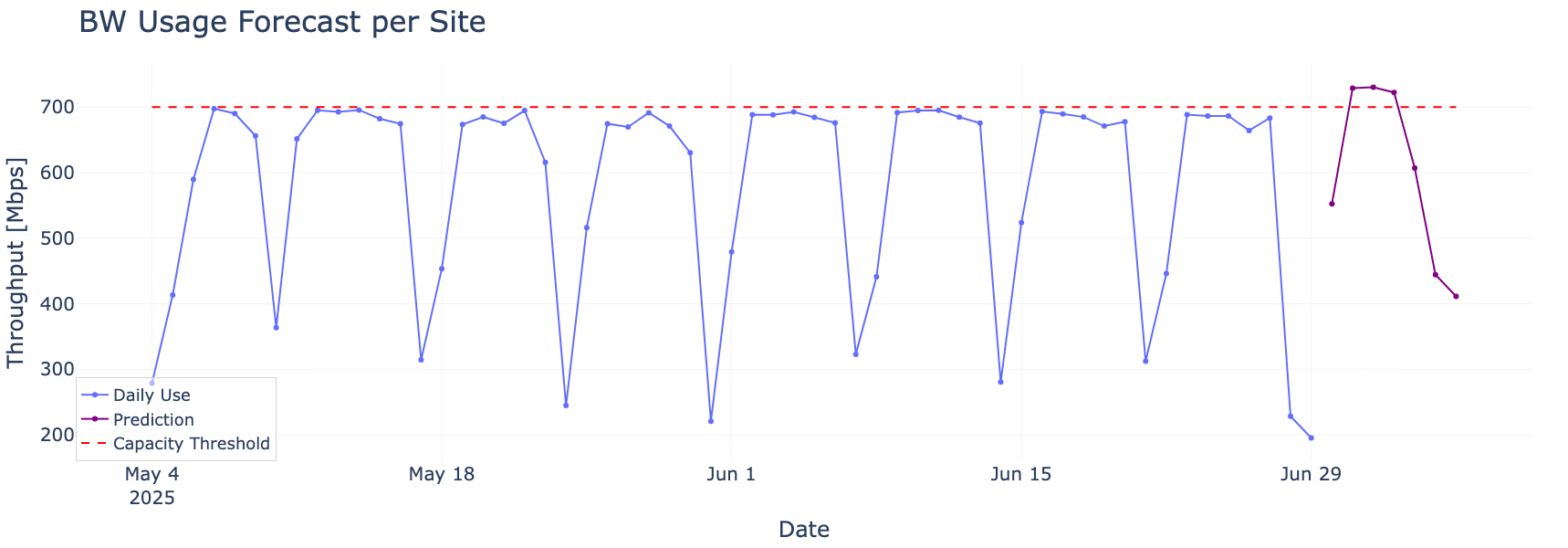
Our research doesn’t stop at CPU. Bandwidth usage is another key area where predictive insights are vital. In Figure 4, we examine how daily bandwidth patterns can help forecast potential capacity threshold breaches. By combining observed usage trends with forecasting models, we can issue early warnings to prevent cost surprises or service disruptions before they occur.
A predictive AI networking model identifies an upcoming capacity breach based on weekday usage trends. Early detection gives IT teams time to adjust policies or usage before hitting critical thresholds.
Figure 4. Forecasting Bandwidth Threshold Breaches
AIOps and Predictive AI Networking in the Cato SASE Cloud Platform
The insights we gain through our ongoing AIOps research enhancing Cato SASE Cloud Platform’s real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and proactive alerting. By embedding predictive capabilities into our platform, we enable IT and security teams to detect and resolve issues, like CPU saturation or bandwidth exhaustion, before they disrupt business. While AIOps excels at detecting anomalies and forecasting trends, root cause analysis plays a complementary role, helping uncover the true source of a problem.
Ultimately, this allows teams to focus on what matters most: running the business with confidence and efficiency.
The post AIOps in the Cato SASE Platform: Using Predictive AI Networking to Shift from Reactive to Proactive IT appeared first on Cato Networks.